Economy
Pakistan’s trading partners

There have been questions raised on the extent to which foreign policy of Pakistan should reflect its trading relationships with individual countries, regions, and groups of countries which are members of international organizations? This requires determination of which are the major destinations of the country’s exports, and which are the major origins of our imports? What is the regional and country-wise pattern of our trade surpluses and deficits? And which are the major countries to which our exports have shown faster growth?
The analysis has been undertaken with trade data made available by the SBP in its economic data website. For earlier years, the relevant information has been obtained from the SBP publication, Handbook of Statistics on Pakistan Economy.
The top four export markets of Pakistan in 2020-21 are the EU countries combined, the USA, UK, and China. It is significant that the major destinations of Pakistan’s exports are mostly in Europe and North America. Pakistan has been granted GSP plus status by the European Union with some preferential tariff treatment. Pakistan also has a free trade agreement with China which has been implemented in steps from 2006 onwards.
The combined exports to the 27 EU countries aggregated to $6.4 billion in 2020-21. This represents a share of 25 percent of Pakistan’s total exports. The second largest value of exports is to the USA of $5.0 billion, equivalent to 20 percent of total exports of Pakistan.
The other two relatively large destinations of the country’s exports are the UK and China. Combined, the share of Pakistan’s four major export markets is over 62 percent of total global exports. This highlights the extreme regional concentration of the country’s exports. The share of SAARC countries is only 8 percent, despite presence of the SAFTA free trade agreement. It was somewhat higher when there was trade directly with India.
Turning to the regional distribution of the country’s imports, the sources are more diversified. China is by far the dominant exporter to Pakistan. Imports from China aggregated to $13.2 billion in 2020-21, equivalent to over 25 percent of total imports. The other major exporting countries to Pakistan include the OPEC countries with a share of 24 percent, followed by the EU countries and the USA. Overall, the combined share of these countries is close to 55 percent in total imports of Pakistan.
What has been the growth rate of exports to the major destinations? Between 2012-13 and 2018-19, the fastest cumulative increase over the six years is to the UK of 33 percent, followed by a 32 percent increase to Germany and of 11 percent to the USA. The big declines are to China of 27 percent, to Afghanistan of 37 percent and to the UAE of as much as 57 percent.
By far the largest increase in imports has been from China, which has taken full advantage of the free trade agreement with Pakistan. Between 2012-13 and 2018-19, the cumulative increase has been as much as 133 percent. Now China alone accounts for 30 percent of total imports of Pakistan.
The overall trade deficit of Pakistan was very large in 2020-21 at $26.5 billion, with imports over twice the level of exports. Therefore, the likelihood is high that Pakistan will carry a significant deficit with most of its major trading partners. The country-wise balance of trade is given in the table below.
========================================================================
Table 1
========================================================================
Pakistan's Trade Balance with Major Trading Partners, 2020-21
($ billion)
========================================================================
Exports to Imports from Balance of Trade
========================================================================
China 2.0 13.2 -11.2
USA 5.0 2.4 3.6
EU Countries 6.5 3.7 2.8
Major OPEC Countries 1.9 9.4 -7.5
Others 10.2 28.7 -18.5
========================================================================
Total 25.6 52.1 -26.5
========================================================================
Pakistan has a very large trade deficit with China, equivalent to 42 percent of its global deficit. The deficit has been growing rapidly. Pakistan’s exports to China have been declining while imports have shown fast growth. Today, China’s exports to Pakistan are six times its imports from Pakistan. The time has come for a review of the implementation of the 2006 Trade Agreement between Pakistan and China. Pakistan needs to seek more quid pro quo from China.
The trade surplus with two major trading partners – the USA and the EU countries – is of $3.6 billion and $2.8 billion, respectively. These are the bigger markets, especially for textile products. The trading relationship with these countries needs to be preserved and built upon.
Pakistan has preferential access to the EU market through the GSP plus programme since 2014. This allows a large share of Pakistan’s exports to enter EU countries free of duty. Two criteria must be met for continuation of this facility. First, GSP-covered imports should be less than 2 percent of EU’s imports from all GSP beneficiaries. The share currently of Pakistan is 1.6 percent. Second, the seven largest GSP covered products must account for at least 75 percent of Pakistan’s total GSP covered exports to the EU. The share currently of these products is 94 percent.
Further, Pakistan has had to ratify 27 core international conventions and subscribe to binding commitments to implement them effectively. These are mainly UN and ILO conventions and other conventions on environment. The GSP status of Pakistan is periodically reviewed by the EU. Weak areas of implementation by Pakistan relate to gender inequality, workers’ rights, and the presence of child workers.
There has been some focus recently on Pakistan’s trading relationship with Russia. The current volume of trade between the two countries is small with $163 million of exports and $593 million of imports. The imports are largely of wheat. Now with the international trade sanctions on Russia following the invasion of Ukraine, new sources of wheat will have to be found when the quantity required could rise to almost 5 million tons given the failure of the current wheat crop.
Via BR
Discover more from The Monitor
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Analysis
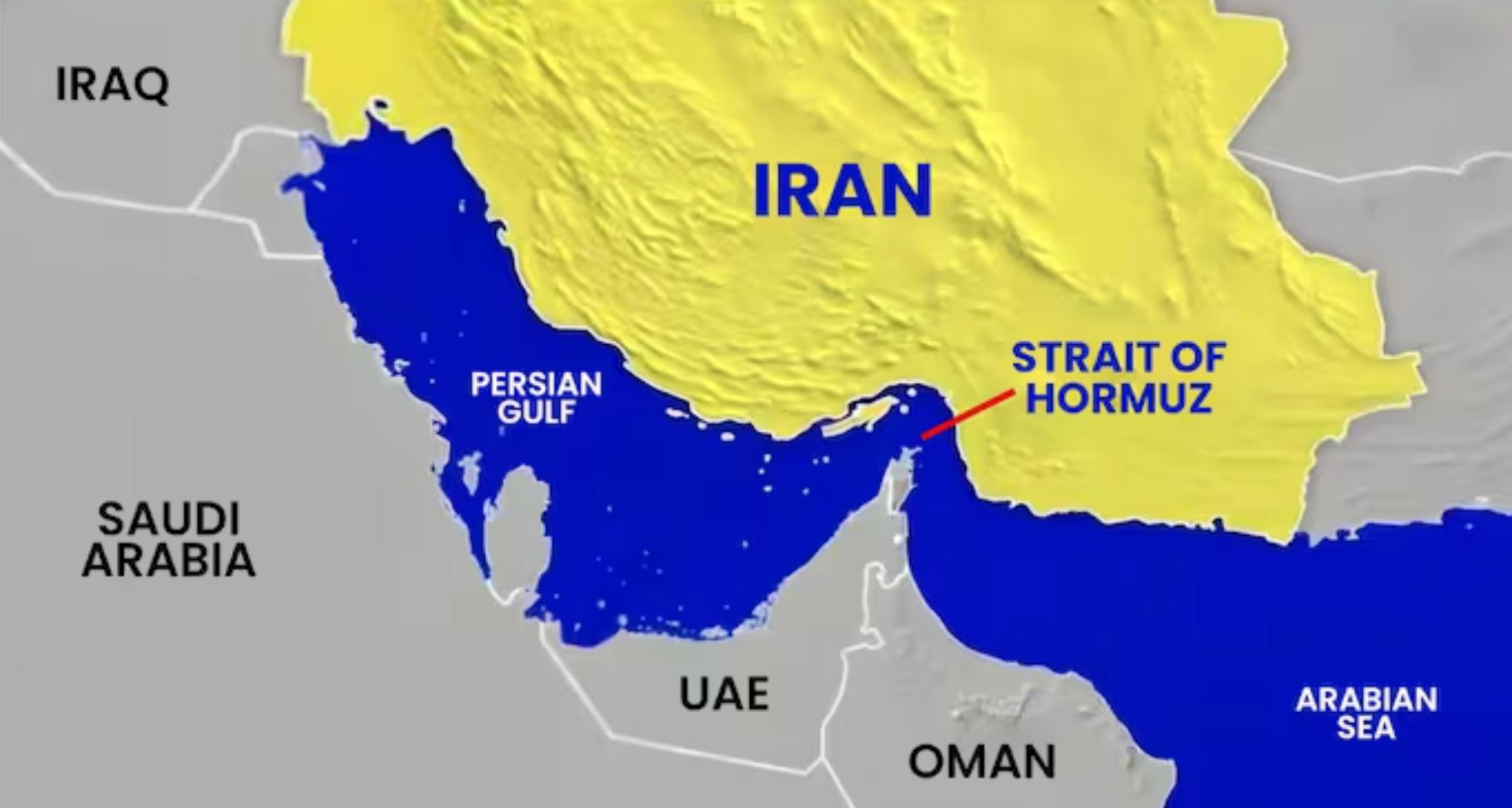
Brent Crosses $100 as Indian Tanker Path Corrected Near Strait of Hormuz

A single misread ship position sent oil markets through a psychological threshold. What it reveals about the fragility wired into global energy supply chains — and why $100 crude may now be the floor, not the ceiling.
By the time New York trading desks were reaching for a second coffee, Brent crude for May delivery had quietly crossed a number that carries outsized psychological weight in commodity markets: one hundred dollars per barrel. At 10:55 a.m. CDT (15:55 GMT), the benchmark stood at $101.83, up $1.37 or 1.36% on the session and on course for a weekly advance. U.S. West Texas Intermediate for April trailed in its wake at $96.26, adding 53 cents, or 0.55%, and likewise pointing to a positive close for the week.
The proximate catalyst was, on its face, almost comedically narrow: a misreading of the navigational position of a single Indian-flagged oil tanker — the Jag Prakash — carrying gasoline bound for Africa. An Indian government official had indicated the vessel was transiting through the Strait of Hormuz, triggering an immediate spike in risk premiums. Within the hour, that account was corrected: the Jag Prakash was, in fact, moving east of the strait, well within the Gulf of Oman, on a route that had never taken it through the chokepoint at all.
Yet Brent held its gains. And that, more than any individual data point, tells you precisely where the global oil market stands in the spring of 2026.
Table of Contents
The Geopolitical Kindling Beneath Every Price Tick
To understand why a single tanker’s GPS coordinates could move a benchmark priced across millions of barrels, you first need to understand what the market is already pricing. The Strait of Hormuz — the narrow passage between Iran and Oman through which roughly 21 million barrels per day flow, representing approximately 20% of global oil trade and one-third of globally traded liquefied natural gas — is not, at this moment, operationally closed. But it is conceptually contested in ways not seen since the tanker wars of the late 1980s.
The escalating U.S.-Israeli military posture toward Iran, following the multilateral strikes on Iranian nuclear infrastructure that defined the first quarter of 2026, has permanently altered how shipping insurers, freight brokers, and portfolio managers assess passage risk through the Gulf. War-risk insurance premiums for Hormuz-transiting vessels have risen sharply since January, according to market participants familiar with Lloyd’s of London pricing. Iranian naval exercises near Abu Musa island have added operational uncertainty. Every tanker departure from Ras Tanura and Kharg Island now carries a geopolitical footnote.
In this environment, the market’s hair-trigger sensitivity to anything resembling a confirmed Hormuz incident is entirely rational — and almost certainly permanent for as long as the current Iranian standoff remains unresolved.
Market Reaction and the Psychology of $100
The $100 threshold for Brent crude is not merely arithmetical. It is behavioral. Crossing it triggers algorithmic buying programmes, resets inflation expectations in central bank models, and — critically — shifts the language of corporate earnings calls, central bank minutes, and finance ministry briefings from “elevated energy costs” to “oil shock.” The semantics matter because they change policy.
“One hundred dollars is where the macro conversation changes,” a senior European macro strategist noted in a client note circulated Thursday. “Below it, energy is a headwind. Above it, energy becomes the story.”
Real-time market data as of the session snapshot:
- Brent May futures: $101.83 (+1.36%)
- WTI April futures: $96.26 (+0.55%)
- Weekly trajectory: Both benchmarks on course for positive weekly close
- Brent premium to WTI: ~$5.57 — widened from the 2025 average of ~$4.10, reflecting elevated Hormuz/Middle East risk embedded in waterborne crude
The WTI-Brent spread’s expansion is itself analytically significant. It suggests the market is not simply pricing a generalised demand impulse — U.S. domestic fundamentals remain broadly stable — but rather a specific maritime and geopolitical risk premium attached to Middle Eastern waterborne crude, precisely the grades most at risk from any Hormuz disruption.
The Jag Prakash Correction — What Actually Happened
The Jag Prakash is an India-flagged product tanker operating in the broader Gulf of Oman and Indian Ocean trade corridor. On Friday morning, an Indian government official communicated that the vessel — carrying a cargo of gasoline (motor spirit) bound for Africa — was in motion near the Strait of Hormuz. The phrase “near the Strait of Hormuz” was initially interpreted by wire services and trading desks alike as implying passage through the strait itself, which would have represented the first confirmed unescorted commercial transit of a vessel carrying hydrocarbons through the waterway since Iranian naval harassment incidents in February.
Within approximately 45 minutes, a corrected statement clarified that the tanker was operating east of the strait, in the Gulf of Oman, on a route that bypasses the chokepoint entirely. The vessel had not transited the Strait of Hormuz. It was — and remained — on a conventional eastward trade arc.
The episode is a case study in information velocity and market fragility. It took less than an hour for a navigational miscommunication to push a globally traded commodity benchmark through a psychologically significant price level. It took the same amount of time for the correction to fail to bring prices back down.
That asymmetry — sharp spikes on bad news, sticky prices on corrections — is the defining characteristic of a market trading in a state of persistent latent anxiety.
Economic Ripple Effects: India, Asia, and the Inflation Transmission Chain
For India specifically, the episode carries layered significance that transcends a single tanker’s position. India is now the world’s third-largest oil importer, having surpassed Japan, and its import bill is denominated overwhelmingly in U.S. dollars against a rupee that remains sensitive to current-account deterioration. Every sustained $10/bbl increase in Brent crude adds approximately $12–14 billion annually to India’s import bill at current consumption volumes, according to estimates consistent with Ministry of Petroleum modelling frameworks.
The Jag Prakash incident, and the broader sensitivity it reveals, matters to New Delhi for three reasons. First, Indian refiners — including Indian Oil Corporation, Bharat Petroleum, and Hindustan Petroleum — have aggressively expanded their purchase of discounted Russian Urals crude since 2022, partly to insulate the country from Middle Eastern supply disruptions. But Russian crude still flows through waters adjacent to Iran’s sphere of influence, and a genuine Hormuz closure would reshape global tanker routing in ways that affect even non-Hormuz cargoes through port congestion and freight-rate contagion.
Second, India’s downstream product exports — including the Jag Prakash‘s gasoline cargo destined for Africa — are a growing source of foreign exchange earnings. Disruption to product tanker routes depresses those margins. Third, and most structurally: India’s inflation dynamics are acutely oil-sensitive. The Reserve Bank of India’s rate-setting calculus is already complicated by food price volatility; a sustained Brent price above $100 would likely delay any easing cycle and sustain borrowing costs for an economy that badly needs cheaper capital.
Across the broader Asian importers — Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Bangladesh, Pakistan — the calculus is similarly unfavourable. These economies collectively import over 20 million barrels per day, and unlike the United States, they have no meaningful domestic production buffer. Asian energy security anxiety, already elevated after the 2022 gas crisis in Europe, would intensify sharply if Hormuz were genuinely disrupted.
What Happens Next: Analyst Outlook and Strategic Implications
The immediate consensus from energy analysts is that the Jag Prakash correction removes the specific trigger for Friday’s move but does nothing to remove the underlying conditions that made markets so reactive in the first place. Several dynamics are worth watching in the coming weeks:
- Iranian naval posturing: Tehran has limited but real ability to complicate Hormuz transits without formally closing the strait — harassment, shadow tanker tactics, drone surveillance of flagged vessels. Any escalation in this grey zone will maintain the risk premium.
- OPEC+ supply discipline: The cartel’s current production agreement has kept supply deliberately tight. There is no indication that Saudi Arabia or the UAE is prepared to unilaterally release capacity to offset geopolitical risk premiums — indeed, Riyadh benefits from prices above $90/bbl for budget equilibrium.
- U.S. strategic petroleum reserve posture: Washington drew the SPR to historic lows in 2022–23 and has only partially replenished it. Deploying it again as a political tool faces both physical constraints and credibility costs.
- Shipping insurance: Lloyd’s and the broader war-risk market may begin pricing Hormuz transits as structurally elevated regardless of day-to-day incident data, effectively building a permanent premium into Middle Eastern crude.
Implications for Global Markets
The Jag Prakash episode will be remembered — if at all — as a footnote in the oil market’s 2026 narrative. The correction came quickly, and no cargo was disrupted, no vessel was damaged. But its significance lies precisely in the speed and magnitude of the market’s initial reaction, and in the stubbornness of prices even after the facts were clarified.
We are operating in an oil market structurally priced for disruption. The geopolitical architecture that underwrote the relative stability of Hormuz transits for four decades — U.S. naval predominance, Iranian diplomatic containment, and the tacit mutual interest of all parties in preserving commercial flows — is under greater stress today than at any point since the tanker war era. That stress is now reflected not just in forward curves and options skew but in the market’s neurological response time to ambiguous information.
For central banks in Frankfurt, London, Delhi, and Tokyo, the message is uncomfortable but unambiguous: $100 Brent is not a crisis. It is, for now, the new normal. The question is not whether energy prices will complicate monetary policy — they already are — but how long policymakers can sustain the fiction that supply-side geopolitical shocks are “transient” in a world where the transit chokepoints themselves have become contested terrain.
For corporate treasurers at airlines, petrochemical firms, and shipping conglomerates, the practical implications are already arriving in hedging desks and procurement contracts. For governments in net-importing economies — and there are far more of those than net exporters — the fiscal arithmetic is tightening with every week that Brent holds above the century mark.
The Jag Prakash was east of Hormuz all along. But the anxiety that read its position otherwise is not going anywhere.
Discover more from The Monitor
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Analysis
Iran Vows to Keep Strait of Hormuz Closed: Mojtaba Khamenei’s First Statement Signals Escalation as Oil Surges Past $100
Flames from the Safesea Vishnu illuminated the night sky over the Khor Al Zubair Port near Basra this week, painting a terrifying picture of a global economy catching fire. The US-owned, Marshall Islands-flagged tanker was loaded with 48,000 metric tonnes of naphtha when a remote-controlled explosive boat rammed its hull. It was a precise, devastating strike.
Half a continent away, in a secure and undisclosed bunker, the shadow of a newly minted leader loomed large. On Iranian state television, the studio was eerily devoid of its usual bombast. Instead, a solemn newsreader stared into the camera to deliver the words of an unseen man. The message was clear: Iran Strait of Hormuz closed Mojtaba Khamenei is not just a trending headline; it is the new geopolitical reality.
As global markets spiral and the death toll from the March 2026 conflict approaches 2,000, the world is waking up to a harsh truth. The targeted assassination of Ali Khamenei during Operation Epic Fury on February 28 has not brought capitulation. Instead, it has ignited a powder keg.
[related: 2026 Middle East Conflict Complete Timeline]
Table of Contents
Mojtaba Khamenei’s Defiant Message: Revenge and the Hormuz Lever
The world waited with bated breath for the Mojtaba Khamenei first statement. Following the joint US-Israeli strikes that killed his father and several family members, the 56-year-old newly appointed Supreme Leader had vanished from public view, reportedly nursing severe injuries. When the silence broke on Thursday, the tone was uncompromising.
Read by a proxy on state TV, the statement confirmed that the Strait of Hormuz must remain closed to pressure Tehran’s adversaries. Mojtaba described the waterway as an essential “lever” of leverage.
But the address was more than an economic threat; it was a deeply personal declaration of war. Iran new supreme leader vows revenge, specifically citing the tragedy at the Minab girls’ school, where BBC News reported a missile strike killed 168 people, including over 110 children.
“We will take war reparations from the enemy for the war it imposed on us,” the statement read, demanding total financial and blood compensation.
To understand the rapid descent into chaos, one must look at the unprecedented pace of escalation:
The March 2026 Escalation Timeline:
- February 28: US and Israeli forces launch Operation Epic Fury, killing Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei and triggering immediate regional shockwaves.
- March 2: The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) formally declares the Strait of Hormuz “sealed,” drastically reducing daily ship transits from 100 to under 30.
- March 4: Iran claims total control of the Strait; Reuters confirms insurance war-risk premiums make transit economically impossible.
- March 11: The devastating attack on the Safesea Vishnu near Basra kills an Indian sailor, signaling a severe geographic expansion of the conflict.
- March 12: Mojtaba Khamenei issues his first national address, demanding the immediate closure of all US military bases in the Middle East.
Tankers Ablaze in Basra and the Gulf – A Step-Up in Asymmetric Warfare
The strike on the Safesea Vishnu proves that Tehran’s reach extends far beyond the narrow chokepoint of Oman and Iran. The Revolutionary Guards tanker attacks Basra show a tactical shift: Iran is now willing to strike deep within the territorial waters of neighboring states to paralyze maritime trade.
According to The Financial Times, the unmanned, white explosive speedboat that hit the tanker was part of a broader, highly sophisticated asymmetric warfare strategy. By utilizing fast-attack drone boats, retrofitted commercial ships, and heavily armed tunnel networks along the coast, the IRGC has effectively neutered the conventional naval superiority of the US Fifth Fleet.
But the maritime domain is only half the battle. This week, we also witnessed a massive volley of Hezbollah rockets Israel March 2026. Launching “Operation The Devouring Storm,” Hezbollah fired over 100 rockets toward northern Israel, triggering sirens in Haifa, Acre, and Tel Aviv.
This multi-front strategy relies on the following asymmetric tactics:
- Swarm Tactics: Dozens of autonomous sea drones deployed simultaneously to overwhelm missile defense systems on commercial and military vessels.
- Proxy Mobilization: Synchronized artillery and rocket fire from Hezbollah in Lebanon and Houthi rebels in Yemen.
- Covert Mining: The deployment of bottom and moored naval mines across shipping lanes, creating a “hellscape” for any vessel attempting passage.
Oil Prices Soar Above $100: The Biggest Energy Shock in History
The economic fallout has been immediate and brutal. The intersection of the Iran war oil prices 2026 narrative and actual market panic has pushed Brent Crude to a terrifying peak of $119 a barrel earlier this week, currently hovering violently above the $100 threshold.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) has already labeled this the “biggest disruption in history.” While emergency reserves have been tapped, Bloomberg notes that the sheer volume of global energy supplies disrupted Iran—roughly 20% of the world’s liquefied natural gas and 27% of maritime crude—cannot be replaced by strategic petroleum reserves alone.
The cascading effects on the global economy are severe:
- Inflation Resurgence: Shipping costs have skyrocketed by 400% as vessels reroute around the Cape of Good Hope, guaranteeing a spike in consumer goods.
- Industrial Paralysis in Asia: China and Japan, heavily reliant on Gulf crude, are already dipping into emergency industrial reserves.
- European Energy Crisis: With LNG shipments trapped in Qatar and the UAE, European natural gas futures have jumped, threatening a return to the winter crises of 2022.
The market cannot stabilize as long as the Strait remains an active kill zone.
Geopolitical Fallout: Why Neighbours Must Close U.S. Bases
Perhaps the most alarming element of Thursday’s broadcast was the explicit US bases Middle East closure demand. Mojtaba Khamenei warned neighboring Gulf nations that hosting American military installations effectively makes them active participants in the war.
“All US bases should be immediately closed in the region, otherwise they will be attacked,” the statement read, adding that American promises of protection were “nothing more than a lie.”
This puts nations like Bahrain, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates in an impossible position. The Economist highlights that these countries host critical infrastructure, such as the Al Udeid Air Base in Qatar and the US Fifth Fleet headquarters in Bahrain.
Beijing is watching this closely. China has invested billions in Gulf infrastructure and relies on regional stability for its Belt and Road Initiative. The current paralysis forces China to reconsider its reliance on US maritime security, potentially accelerating a multipolar naval presence in the Indian Ocean. Meanwhile, OPEC finds itself paralyzed, unable to pump enough surplus oil to calm markets without risking the total destruction of its export infrastructure by Iranian missiles.
What This Means for Global Markets and the Trump Administration
In Washington, the political narrative is colliding violently with economic reality. Following the decapitation strike on Ali Khamenei, President Donald Trump claimed a decisive victory, telling supporters, “We already won.” But as Forbes notes, tactical victories do not equate to strategic success.
The administration’s assertion that the US Navy could quickly escort commercial vessels through the Strait has been proven false. The sheer density of asymmetric threats makes escort missions a suicidal gamble for unarmored tankers.
If oil remains above $110 a barrel for more than a quarter, global recession is virtually guaranteed. The Federal Reserve, already battling sticky inflation, will be forced into emergency rate hikes, strangling corporate growth and triggering mass layoffs. The “victory” lap in Washington may soon be drowned out by the cries of a collapsing domestic economy.
The Human Cost and the Path to De-escalation
Beyond the economic charts and geopolitical maneuvering, the human cost is catastrophic. The death toll from the March 2026 conflict is rapidly approaching 2,000. Over 3 million Iranians are internally displaced, fleeing major cities for the rural north, according to The New York Times. On the water, innocent merchant mariners, like the Indian sailor lost on the Safesea Vishnu, are paying the ultimate price for a war they have no part in.
So, what happens if Iran blocks Strait of Hormuz completely and indefinitely? Analysts point to three distinct scenarios for the coming months:
- The Escalation Trap (High Probability): The US attempts a forced reopening of the Strait using massive carpet-bombing of the Iranian coastline. Iran responds by launching ballistic missiles directly at Saudi and Emirati oil refineries, plunging the world into a 1970s-style energy depression.
- The Diplomatic Off-Ramp (Medium Probability): A neutral third party, likely Oman or China, brokers a temporary ceasefire. Iran agrees to let non-US flagged vessels pass in exchange for a halt to American airstrikes and sanctions relief, creating a fragile, heavily armed peace.
- The Grinding War of Attrition (Low Probability): The conflict settles into a low-intensity maritime insurgency. The Strait remains “open” but so dangerous that only state-subsidized fleets dare cross, keeping oil prices permanently elevated and slowly suffocating the global economy.
Mojtaba Khamenei’s first statement has drawn a line in the blood-soaked sand. The leverage of the Hormuz choke point is fully engaged, and the global economy is now hostage to a war that neither side seems able to end.
Discover more from The Monitor
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Analysis
Pakistan’s 5G Era Begins: Pilot Projects Launch Next Week After Record $510 Million Spectrum Auction

Pakistan 5G pilot projects start next week following $507M spectrum auction. How 5G will change internet speeds Pakistan from 4 Mbps to 20 Mbps—analysis of rollout challenges.
Standfirst: After years of regulatory delays and industry scepticism, Pakistan has concluded its most lucrative spectrum auction to date, netting $510 million and paving the way for pilot 5G launches from next week. IT Minister Shaza Fatima Khawaja tells operators the transition must balance technological leap with the reality of the world’s lowest ARPU—while a new smartphone leasing policy aims to bridge the device gap.
The announcement came not with the usual fanfare of a gleaming telecom expo, but in a packed Islamabad news conference where the mood was one of guarded optimism. Flanked by PTA Chairman Hafeez Ur Rehman and representatives from Jazz, Ufone, and Zong, Minister for Information Technology and Telecommunication Shaza Fatima Khawaja delivered the news that an industry—and a nation of 240 million—had been awaiting for half a decade.
“I was very happy to hear the day before yesterday that some of our operators are ready for 5G services,” she told reporters on March 12, 2026. “So, its pilot will start in some cities next week. And in the next six to eight months, in five of our capitals of all provinces and in the federal capital, 5G services will be available to all of you people.”
Behind that understated delivery lies a telecom auction that defied expectations. When the Pakistan Telecommunication Authority (PTA) opened bidding on March 10, few anticipated the ferocity of competition that would follow. Across three rounds of electronic bidding, conducted via a secure Electronic Auction System with live results broadcast on Pakistan Television, three operators—Jazz, Ufone, and Zong—contested 480 MHz of spectrum across six bands. The result: $510 million in government revenue, with Jazz emerging as the dominant bidder, securing 190 MHz including the prized 700 MHz band. Ufone claimed 180 MHz, while Zong took 110 MHz.
For context, this surpasses every previous Pakistani spectrum auction. It signals something deeper: after years of circling each other warily, the government and mobile operators have finally found common ground.
Table of Contents
The Auction That Nearly Wasn’t: Inside the $510 Million Spectrum Sale
To understand why this auction represents more than a revenue line, one must revisit the landscape of just eight months ago. At the GSMA’s Digital Nation Summit in Islamabad in August 2025, the industry’s frustrations were laid bare. Julian Gorman, the GSMA’s Head of Asia Pacific, warned that Pakistan risked missing the digital transformation wave entirely, citing “high spectrum prices, heavy sector-specific taxes and regulatory uncertainty” as barriers limiting investment.
The operators had been blunter still. In a report released by the Asian Development Bank in mid-2025, they argued that 5G rollout was “almost impossible” under prevailing conditions. “With the lowest-in-the-world average revenue per user (ARPU), exorbitantly high taxes, low adoption of 4G/smartphones, and multiple other outstanding sector issues, it will be extremely challenging to convince our parent companies to invest in 5G roll out in Pakistan,” the submission read.
What changed? The answer lies in the auction design itself. Speaking at the launch ceremony, Minister Khawaja emphasized that the government had deliberately avoided the temptation to maximise upfront revenues. “The aim is not to maximise upfront auction revenues,” she stated, “but to provide operators with the opportunity to invest in network expansion and infrastructure so that improved and high-quality digital services can be delivered to consumers across Pakistan.”
PTA Chairman Hafeez Ur Rehman reinforced this message, noting that the Authority had taken “consumer-centric regulatory measures, including bringing Right of Way (RoW) charges to zero, in order to facilitate faster network rollout and reduce barriers for telecom operators.”
The result was a delicate compromise: operators secured spectrum at sustainable prices, while the government achieved both revenue targets and a credible path to 5G.
Auction Breakdown: Who Won What
| Operator | Spectrum Acquired | Key Band Secured | Strategic Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jazz | 190 MHz | 700 MHz | Dominant low-band coverage |
| Ufone | 180 MHz | Mid-band | Aggressive challenger |
| Zong | 110 MHz | 2600/3500 MHz | Capacity-focused |
The assignment stage, scheduled for March 12, will determine specific frequency positions within each band, with an additional $3 million expected from position assignment fees.
From 4 Mbps to 20 Mbps: What 5G Actually Means for Pakistani Users
Beyond the boardroom negotiations and spectrum lots, a more fundamental question lingers for Pakistan’s 190 million mobile subscribers: what will 5G actually change?
The government projects that average internet speeds will climb from the current 4 Mbps to approximately 20 Mbps once networks are fully operational. For a country where video streaming often buffers and large file downloads test patience, this leap carries tangible implications. But the transformation runs deeper than faster Netflix queues.
The World Bank’s 2024 report “The Path to 5G in the Developing World” identifies three distinct tiers of 5G value for emerging economies. The first is enhanced mobile broadband—precisely the speed improvement Pakistan now anticipates. The second is ultra-reliable low-latency communications, which enables industrial applications: remote machinery operation, real-time quality control in manufacturing, and precision agriculture. The third, massive machine-type communications, underpins smart city sensors, utility grid management, and logistics tracking.
For Pakistan, with its ambitions of becoming a regional data hub and IT outsourcing destination, the second and third tiers represent the true prize. But they remain distant without corresponding investments in fibre backhaul, data centre capacity, and—critically—devices.
The Smartphone Leasing Gambit: Can Pakistan Bridge the Device Divide?
Here lies the industry’s Achilles heel: you cannot consume 5G on a 4G device, and Pakistan’s smartphone penetration tells a troubling story. According to GSMA data presented at the August 2025 summit, while 68% of Pakistanis own a smartphone, only 29% actively use mobile internet—a usage gap of 52%, the highest among major regional markets. Nearly 40% of mobile users still rely on feature phones.
Enter the “Smartphone for All” initiative, a government-backed leasing scheme announced in February 2026 that now assumes urgent relevance. Under the programme, citizens can acquire smartphones valued between Rs10,000 and Rs100,000 through interest-free instalments spanning three to twelve months, with a minimum 20% down payment. Students, low-income individuals, and professionals are all eligible.
Minister Khawaja has framed the scheme as essential to 5G’s success. “Officials have said the government is also encouraging wider adoption of 5G-compatible devices to support the transition to faster mobile networks, noting that a large share of phones used in Pakistan are locally manufactured while premium models are imported,” Arab News reported following her briefing.
The arithmetic is straightforward: without affordable 5G handsets in Pakistani hands, the billions spent on spectrum will yield little beyond faster connections for an urban elite.
The ARPU Paradox: World’s Lowest Revenue, World-Class Ambition
Yet even if devices materialise, the industry must confront its existential challenge: Pakistan’s average revenue per user (ARPU) remains the lowest globally. Operators extract a fraction of the monthly revenue that Indian or Bangladeshi carriers achieve, and a tiny sliver of developed-world averages. This fundamentally constrains the investment case.
The government has offered assurances that consumer packages will not see immediate price hikes, but operators face an unsustainable calculus. Nikkei Asia noted that “some experts skeptical about demand” remain unconvinced that Pakistani consumers will pay premiums for 5G when 4G meets most basic needs.
The sector’s tax burden compounds the challenge. Combined taxes on mobile usage reach 33%, among the highest in the region, increasing consumer costs and suppressing demand. The GSMA has repeatedly called for rationalisation, arguing that lower taxes would stimulate usage, expand the taxable base, and ultimately increase government revenues.
For now, the government has signalled no immediate tax relief. But Minister Khawaja’s emphasis on sustainable sector growth suggests a recognition that the current model cannot persist indefinitely.
International Interest: Why Mobile World Congress Is Watching Pakistan
Despite these structural headwinds, Pakistan’s 5G auction has attracted international attention that extends far beyond its borders. At the recent Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, multiple inquiries centred on the Pakistani market—its scale, its trajectory, and its potential as a manufacturing hub.
The interest is not merely academic. With India’s 5G rollout now well advanced and Bangladesh preparing its own auction, investors view South Asia as the next great connectivity battleground. Pakistan, with its young population, rising IT exports, and strategic location, represents a critical piece of that puzzle.
The armed forces’ vacation of spectrum in the 700 MHz band proved pivotal in unlocking this interest. That band, prized for its propagation characteristics that enable wider coverage with fewer towers, formed the cornerstone of Jazz’s successful bid. It also signals a mature approach to civil-military coordination on digital infrastructure—a prerequisite for any emerging market seeking serious foreign investment.
Regional Scorecard: Pakistan vs. India, Bangladesh, Nigeria
How does Pakistan’s 5G entry compare with its peers?
India conducted its 5G auctions in 2022, raising $19 billion and launching services later that year. By early 2026, coverage extends to most major cities, though adoption remains constrained by device costs similar to Pakistan’s. Bangladesh has announced plans for 2026 auctions but faces political uncertainty. Nigeria, Africa’s largest economy, launched 5G in 2022 and now counts over two million subscribers.
Pakistan thus enters the 5G race as a late adopter but not a laggard. Its advantage lies in learning from others’ mistakes: India’s high reserve prices initially deterred participation, requiring subsequent reductions. Pakistan’s more measured approach, emphasising sustainable pricing, reflects those lessons.
Yet Pakistan also carries unique burdens. No other major market combines such low ARPU with such high taxation. No other faces the same intensity of energy reliability challenges, with operators paying commercial tariffs for power while enduring frequent outages.
The Economic Multiplier: Can 5G Really Add $10 Billion to GDP?
Government briefings have cited a target of $10 billion in GDP contribution from 5G over the next five to seven years. The figure derives from Ericsson’s modelling of 5G economic impacts in emerging markets, which estimates that every dollar invested in 5G infrastructure generates multiples in downstream economic activity.
The transmission mechanism runs through several channels: productivity gains in manufacturing and logistics, new business models enabled by reliable high-speed connectivity, expanded IT exports, and formalisation of economic activity. Each requires not just spectrum, but the entire ecosystem of fibre, data centres, skills, and regulation.
Here, the GSMA’s “Unlocking Pakistan’s Digital Potential” report provides a sobering checklist of remaining reforms: releasing additional mid-band spectrum, permitting spectrum sharing and trading, reducing sector-specific taxes, expanding anti-fraud initiatives, and accelerating digital literacy programmes, especially for women and rural communities.
The Road Ahead: Pilots, Politics, and Patient Capital
Next week’s pilot launches in select cities will mark Pakistan’s first encounter with live 5G networks. For the technologists who have laboured through years of policy uncertainty, it will be a moment of vindication. For consumers, the immediate experience may underwhelm: early pilots typically showcase capabilities rather than deliver ubiquitous coverage.
The true test comes in the six-to-eight month window that follows, as operators extend coverage to provincial capitals and—eventually—secondary cities. By year-end 2026, Pakistan will have a clearer sense of whether its 5G gamble pays off.
Minister Khawaja captured the balancing act required when she addressed operators alongside the PTA chief. “The auction process was designed to protect the rights of both the industry and consumers,” she said. That compact—sustainable returns for operators, affordable access for citizens, and reasonable revenues for the state—represents the holy grail of telecommunications policy.
Pakistan has secured the spectrum. It has unlocked the investment. It has signalled, through the smartphone leasing scheme, a recognition that connectivity without devices is infrastructure without purpose. Now begins the harder work: building the networks, acquiring the customers, and proving that 5G can deliver not just faster speeds, but genuine economic transformation.
For a nation of 240 million, with the world’s lowest ARPU but among its highest reserves of youthful ambition, the stakes could scarcely be higher.
Discover more from The Monitor
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
-

 Featured5 years ago
Featured5 years agoThe Right-Wing Politics in United States & The Capitol Hill Mayhem
-

 News4 years ago
News4 years agoPrioritizing health & education most effective way to improve socio-economic status: President
-

 China5 years ago
China5 years agoCoronavirus Pandemic and Global Response
-

 Canada5 years ago
Canada5 years agoSocio-Economic Implications of Canadian Border Closure With U.S
-

 Democracy5 years ago
Democracy5 years agoMissing You! SPSC
-

 Conflict5 years ago
Conflict5 years agoKashmir Lockdown, UNGA & Thereafter
-

 Democracy5 years ago
Democracy5 years agoPresident Dr Arif Alvi Confers Civil Awards on Independence Day
-

 Digital5 years ago
Digital5 years agoPakistan Moves Closer to Train One Million Youth with Digital Skills



















