Analysis
Israel-Palestine: Negotiations Are the Only Way to Peace
The Israel-Palestine conflict is one of the most intractable and long-running conflicts in the world. It has raged for over a century, with no end in sight. The conflict has claimed the lives of hundreds of thousands of people and displaced millions more. It has also caused immense suffering and hardship. There are many different perspectives on the conflict, and it is important to understand all of them in order to find a solution. However, there is one thing that is clear: more bloodshed will never resolve the conflict.
Table of Contents
Background
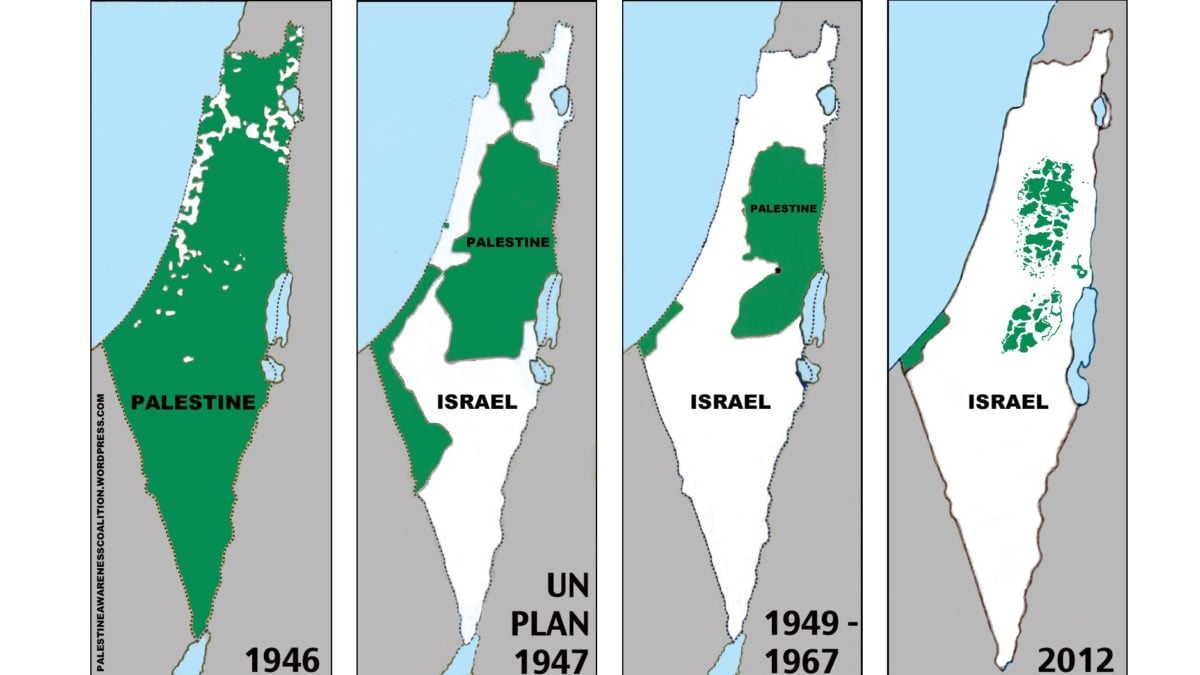
The Israel-Palestine conflict has its roots in the late 19th century, when the Zionist movement began to call for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine. At the time, Palestine was part of the Ottoman Empire and was home to a majority of Arabs.
The Zionist movement gained momentum in the early 20th century, as a result of the rise of anti-Semitism in Europe. In 1917, the British government issued the Balfour Declaration, which expressed support for the establishment of a Jewish national home in Palestine.
After World War I, the Ottoman Empire collapsed and Palestine was placed under British rule. During this period, the Jewish population in Palestine grew significantly due to immigration from Europe.
In 1947, the United Nations voted to partition Palestine into two states, one Jewish and one Arab. The Jewish community accepted the plan, but the Arab community rejected it.
In 1948, Israel declared its independence. The Arab countries that had rejected the partition plan invaded Israel, but they were defeated.
As a result of the war, hundreds of thousands of Palestinians were displaced from their homes. These refugees and their descendants have become a major issue in the conflict.
The Two-State Solution
The two-state solution is the most widely accepted international solution to the Israel-Palestine conflict. It calls for the establishment of two independent states, one Israeli and one Palestinian, living side-by-side in peace and security.
There is broad support for the two-state solution among the international community, including the United States, the European Union, and the United Nations. However, there is no consensus on the terms of a two-state solution, and both the Israeli and Palestinian governments have been reluctant to make the necessary compromises.
The One-State Solution
The one-state solution is a less widely accepted solution to the Israel-Palestine conflict. It calls for the establishment of a single, bi-national state in Palestine.
Proponents of the one-state solution argue that it is the only way to ensure true equality and justice for all Palestinians. They also argue that it is the only way to guarantee a sustainable and peaceful solution to the conflict.
Opponents of the one-state solution argue that it is unrealistic and unworkable. They argue that it would be impossible to create a single, bi-national state that would be acceptable to both Israelis and Palestinians. They also argue that it would lead to increased violence and instability in the region.
The Current Situation
The current situation in the Israel-Palestine conflict is dire. There is a lack of trust between the two sides, and both sides are unwilling to make the necessary compromises.
The Israeli government has built a separation barrier that cuts through the West Bank, isolating Palestinian communities and making it difficult for them to access essential services. The Israeli government has also imposed a blockade on the Gaza Strip, which has caused a humanitarian crisis.
The Palestinian Authority (PA), which governs the West Bank, is weak and corrupt. The PA has been unable to provide basic services to its people and has been unable to prevent Hamas from taking control of the Gaza Strip.
Hamas is a terrorist organization that has launched thousands of rocket attacks on Israel. Hamas has also been responsible for the deaths of hundreds of Israeli civilians.
The Way Forward
The only way to resolve the Israel-Palestine conflict is through a negotiated settlement. Both sides need to be willing to make compromises and to build trust.
The international community can play a role in facilitating a negotiated settlement. However, the international community cannot force a solution on the parties. The only way to achieve a lasting peace is for the Israelis and Palestinians to reach an agreement that they are both willing to live with.
Analytical Approach
The Israel-Palestine conflict is a complex and multifaceted conflict. There is no single solution that will satisfy all parties. However, there are some key steps that can be taken to move towards a resolution.
The first step is to build trust between the two sides. This will require both sides to make concessions and to show that they are committed to a peaceful solution.
The second step in resolving the Israel-Palestine conflict is to address the root causes of the conflict. These root causes include:
- The Israeli occupation of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip
- The Palestinian refugee problem
- The status of Jerusalem
- The security concerns of both Israelis and Palestinians
The Israeli occupation of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip is one of the most pressing issues in the conflict. The occupation has caused widespread economic and social hardship for Palestinians. It has also led to a cycle of violence and mistrust.
The Palestinian refugee problem is another major issue in the conflict. There are currently over six million Palestinian refugees living in the Middle East. These refugees have a right to return to their homes, but Israel has refused to allow them to do so.
The status of Jerusalem is a third major issue in the conflict. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their capital. This issue is highly symbolic and religious, and it is very difficult to resolve.
The security concerns of both Israelis and Palestinians are also a major issue in the conflict. Israelis fear Palestinian terrorism, while Palestinians fear Israeli military aggression.
Possible Solutions
There are a number of possible solutions to the Israel-Palestine conflict. However, all of these solutions require compromises from both sides.
One possible solution is the two-state solution. This solution would involve the establishment of two independent states, one Israeli and one Palestinian, living side-by-side in peace and security.
Another possible solution is the one-state solution. This solution would involve the establishment of a single, bi-national state in Palestine.
Challenges
There are a number of challenges to resolving the Israel-Palestine conflict. These challenges include:
- The lack of trust between the two sides
- The unwillingness of both sides to make the necessary compromises
- The complexity of the issues involved
- The role of regional and international actors
The lack of trust between the two sides is one of the biggest challenges to resolving the conflict. Both sides have been traumatized by the violence of the past, and they are both deeply suspicious of each other.The unwillingness of both sides to make the necessary compromises is another major challenge. Both sides have entrenched positions, and they are both reluctant to give up anything.
The complexity of the issues involved is also a challenge. The conflict is not just about land and borders. It is also about religion, nationalism, and identity. The role of regional and international actors is also a challenge. Some regional and international actors have a vested interest in perpetuating the conflict.The Israel-Palestine conflict is one of the most intractable and long-running conflicts in the world. However, it is important to remember that all conflicts can be resolved, given the will and the courage to do so.
The only way to resolve the Israel-Palestine conflict is through a negotiated settlement. Both sides need to be willing to make compromises and to build trust. The international community can play a role in facilitating a negotiated settlement, but it cannot force a solution on the parties. The only way to achieve a lasting peace is for the Israelis and Palestinians to reach an agreement that they are both willing to live with.
Analytical Approach: A Case Study
One way to analyze the Israel-Palestine conflict is to use a case study approach. This approach involves examining the conflict in detail, including its history, its root causes, and its impact on the people involved.
A case study of the Israel-Palestine conflict would need to consider the following factors:
- The history of the conflict, including the Zionist movement, the Balfour Declaration, the British Mandate, the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, and the subsequent Israeli occupation of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip.
- The root causes of the conflict, including the Israeli occupation, the Palestinian refugee problem, the status of Jerusalem, and the security concerns of both Israelis and Palestinians.
- The impact of the conflict on the people involved, including the loss of life, the destruction of property, and the psychological and emotional trauma.
A case study of the Israel-Palestine conflict would also need to consider the role of regional and international actors. These actors include the United States, the European Union, the United Nations, and the Arab countries.
Conclusion
The Israel-Palestine conflict is a complex and multifaceted conflict. There is no easy solution. However, by understanding the conflict and its root causes, we can start to develop a more informed and nuanced approach to resolving it.A case study approach can be a useful tool for understanding the Israel-Palestine conflict. By examining the conflict in detail, we can gain a better understanding of its history, its causes, and its impact on the people involved.
Discover more from The Monitor
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Analysis
The 400 Million Barrel Question: Can the IEA’s Historic Reserve Release Save the Global Economy from Iran’s Energy War?

With the Strait of Hormuz effectively closed and 20% of global oil supply offline, the IEA’s unprecedented 400 million barrel intervention buys time—but at what cost? Analysis from the front lines of the world’s most dangerous energy crisis.
The room fell quiet before he finished the sentence. On the morning of March 10, 2026, Fatih Birol stepped to the podium at the International Energy Agency’s glass-and-steel headquarters on the Rue de la Fédération in Paris and spoke the words that every trader, finance minister, and energy strategist in the building had been dreading for weeks. Behind him, digital displays flickered with Brent crude’s near-vertical trajectory—$114 per barrel and still climbing. In the front row of the press gallery, veterans who had covered the 1979 revolution and the 2008 price spike sat with their notebooks open, saying nothing. They had seen shocks before. They had not seen this.
“The International Energy Agency today authorized the largest emergency oil reserve release in its 52-year history—400 million barrels,” Birol announced, his voice measured against the magnitude of the number, “more than double the response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, aimed at countering what we are calling the most significant supply disruption since the founding of this agency.”
The statement landed like a confession. That the IEA—born in the trauma of the 1973 Arab oil embargo precisely to prevent days like this—had to deploy more firepower than it ever has before was itself the news. The release was unprecedented. So was the crisis that demanded it.
But the question that hung in the air of that Paris briefing room, and that now hovers over every energy ministry, hedge fund war room, and central bank modeling desk on the planet, is whether this unprecedented intervention can actually stabilize markets—or whether it is merely the opening bid in a negotiation with gravity: a recognition that some energy shocks cannot simply be stockpiled away.
Table of Contents
The Anatomy of the Shock
To understand why this moment is categorically different from previous Middle East crises, one must first confront the arithmetic of the Strait of Hormuz. The 21-mile-wide chokepoint between Iran and Oman carries approximately 20% of all globally traded oil—roughly 17 to 21 million barrels per day under normal conditions. Since Iran’s escalatory campaign began in earnest following the February 28 strikes, export volumes have collapsed to less than 10% of pre-war levels. The Strait has not been “closed” in any formal legal sense. It has been made functionally impassable by a combination of Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps harassment, insurance market withdrawal, and the spectacle of burning tankers visible on satellite imagery worldwide.
The price response was swift and brutal. Brent crude spiked 40% in the days following the February 28 strikes, touching $114 per barrel—a level last seen during the 2022 Russian invasion premium and before that, only briefly, in the chaotic months of 2008. But the 2022 spike was cushioned by record U.S. shale output and a coordinated IEA release of 182.7 million barrels that helped cap the damage. The cushions available today are thinner.
What makes this crisis strategically different is the sophistication of Iran’s approach. Writing in Foreign Affairs, strategic analyst Robert Pape identified this template as “horizontal escalation”—the deliberate multiplication of exposure across geographies to impose costs disproportionate to any single military action. Iran struck or threatened targets in nine countries hosting U.S. forces or allied infrastructure. The message was as clear as it was devastating: alignment with Washington now carries a quantifiable price tag, denominated in tanker insurance premiums and refining disruptions.
The human texture of this crisis matters as much as the data. The Dubai hotel fire in late February—caused by debris from an intercepted Iranian ballistic missile—killed eleven foreign nationals. Explosions visible from the balconies of Abu Dhabi’s luxury hotels sent a particular kind of signal to the global investor class: the Gulf’s geography of impunity, the quiet assurance that wealth could be parked there safely, was being renegotiated in real time.
The 400 Million Barrel Gamble
The mechanics of the IEA’s action deserve scrutiny, because the gap between the headline number and the operational reality is where markets will find their next trading signal. The 400 million barrel figure represents a coordinated drawdown across all 32 member states. IEA voting rules require consensus for action of this magnitude, which means a single dissenting member could have delayed the response by days or weeks. That unanimous vote, secured within 48 hours of the February 28 strikes, was itself a diplomatic achievement of the first order.
Germany and Austria moved within hours to confirm national participation. Germany will release 2.64 million tons of strategic crude and product reserves. Austria implemented emergency retail pricing controls and announced extensions to its strategic gas reserve mandate. Japan confirmed its drawdown would begin March 16.
But here is what the press releases do not say: this is not a flood of oil. Strategic reserve releases do not work like turning on a tap. The transmission mechanism is as much psychological as physical—and the psychology is complicated by a refining capacity bottleneck that Birol himself acknowledged. “The most important thing,” Birol said, “remains the resumption of normal transit through the Strait. The reserve release buys us time. It does not buy us safety.”
“Once you release them, they don’t exist. Strategic reserves are finite ammunition. You use them once.”
— Nick Butler, former head of strategy, BP
IEA member state strategic holdings stand at approximately 1.2 billion barrels of government stocks plus 600 million barrels held by industry under IEA obligation rules. A 400 million barrel release represents roughly 22% of the combined total—a significant draw that will not be replenished quickly, or cheaply, given current market conditions.
The G7 Calculus and the Politics of Price
The G7 statement expressed “support in principle for proactive measures, including the deployment of strategic reserves” to prevent energy supply disruptions from translating into permanent economic damage. Austria’s energy minister, speaking outside the Vienna chancellery, framed the national measures in terms that resonated beyond technocratic policy: “In a crisis, there must be no crisis winners at the expense of commuters and businesses.”
The IEA was established in 1974 in direct response to the Arab oil embargo—designed by Henry Kissinger as a collective Western instrument for managing exactly this kind of supply-side shock. It has been deployed five times before: the Gulf War in 1991, Hurricane Katrina in 2005, the Libyan civil war in 2011, the COVID recovery crunch in 2021, and the Ukraine invasion in 2022. Each release has been larger than the last. Each crisis has been more structurally complex than the previous one.
The China Factor: Energy Security vs. Strategic Ambiguity
The analysis that competitors are not providing—and that decision-makers genuinely need—concerns Beijing’s posture. China imports more than 55% of its oil from the Middle East, with approximately 13% of total imports sourced directly from Iran. Virtually all of it transits the Strait of Hormuz. By any simple calculus of national interest, China should be among the most motivated actors seeking to restore Hormuz’s functionality. Yet Beijing has not intervened diplomatically, has not conditioned its substantial economic leverage over Tehran, and has not publicly pressured Iran to stand down.
Analyst Yun Sun, writing in Foreign Affairs, has identified the paradox with precision: Chinese strategic disillusionment with Iran has deepened over the past two years. Beijing invested political capital in the “no limits” partnership announcement of 2022, only to watch Iran’s proxies underperform, its retaliatory threats prove hollow, and its revolutionary rhetoric deliver diminishing geopolitical returns. China’s netizens have mocked what they term “performative retaliation.” Iran’s GDP is less than 90% of Israel’s and roughly 25% of Saudi Arabia’s. The Islamic Republic’s actual power has been chronically overstated, and Beijing has noticed.
China’s red line, according to officials briefed on Beijing’s internal modeling, is a Strait closure that cuts off more than 50% of its oil imports for a sustained period. Below that threshold, Beijing prefers strategic ambiguity: quiet pressure on Iran to keep shipping lanes minimally functional, while maintaining public neutrality that preserves diplomatic optionality with all parties.
Historical Echoes: What 1973, 1979, and 2022 Teach Us
Every serious analyst in the IEA briefing room yesterday carried the weight of three prior shocks. The 1973 Arab oil embargo was the IEA’s founding trauma—the moment when Western consumers discovered that energy was not a market commodity but a geopolitical instrument. The price of oil quadrupled in three months. Kissinger’s response—the creation of the IEA as a collective Western energy security architecture—was a masterstroke of institutional design, even if the institution’s tools have been outpaced by the sophistication of subsequent crises.
The 1979 Iranian Revolution introduced the world to frozen assets as a weapon. The $12 billion in Iranian assets blocked by the Carter administration following the hostage crisis opened decades of litigation over extraterritorial sanctions. Today’s debates about frozen Iranian assets, Russian reserves, and the weaponization of the dollar-clearing system are direct descendants of those January 1980 executive orders.
The 2022 Ukraine response—then-record 182.7 million barrels—demonstrated both what IEA coordination could achieve and where its limits lie. But it also taught a harsh lesson in reserve arithmetic: the ammunition is finite, the refilling is slow, and adversaries adapt. The lesson compounds with interest: each successive crisis requires more firepower for diminishing marginal effect. 182.7 million barrels in 2022. 400 million barrels in 2026. The trajectory is not reassuring.
The Unanswerable Questions: Refining, Duration, Escalation
Three structural uncertainties will determine whether yesterday’s announcement is remembered as stabilization or as the revelation of architecture’s limits.
The first is the refining bottleneck. Complex refineries configured for sour Gulf crude cannot easily pivot to light sweet alternatives. Crack spreads have widened dramatically. The strategic reserves release may keep headline crude prices from reaching $140—the psychological threshold at which demand destruction becomes severe—but it may not prevent diesel and jet fuel premiums from rising to levels that damage logistics chains regardless.
The second is duration. If the Hormuz disruption proves to be weeks rather than months, the release performs its intended function: a bridge over the acute phase. If the disruption extends into Q3, the mathematics of reserve drawdown become punishing. Member states would face the prospect of deploying reserves faster than markets can stabilize, creating a secondary crisis of reserve depletion that undermines the very confidence the release was meant to project.
The third—and most consequential—is escalation. Iran has already struck or targeted oil production infrastructure in Saudi Arabia and the UAE. A direct hit on a major Gulf oil field would trigger a supply shock of a different order entirely. At that point, the conversation shifts from reserves management to military deterrence, from Birol’s podium to the Fifth Fleet’s operations center.
The New Energy Doctrine
What yesterday’s announcement ultimately signals is not a solution but a reckoning: the energy security architecture of 1974 has met the hybrid warfare of 2026, and the encounter has been clarifying. Iran’s horizontal escalation strategy has demonstrated something strategists have theorized for decades but rarely seen executed with this level of precision: that a middle power with limited conventional military capacity can inflict systemic pain on a globally integrated economy without winning a single battle.
The path forward is structurally obvious and operationally difficult. Diversification beyond Middle Eastern crude dependency—through expanded U.S. shale production, accelerated LNG buildout, and the long arc of renewable energy transition—is no longer merely economic optimization. It is a national security imperative. But transitions of this scale require decades, not quarters. Reserves buy time. They do not buy safety.
On the morning of March 11, Fatih Birol returned to his office on the Rue de la Fédération. The terminals still flickered. The tankers still sat idle in the Gulf of Oman, their masters awaiting insurance clearance that may not come. In his prepared closing statement on Tuesday, he chose words that were careful and deliberately insufficient: “We will continue monitoring. We stand ready to act.”
Behind him, the screens still showed the number: $114. And behind that number, visible to anyone willing to look, was the question that no release can answer: what happens when the barrels run out?
Discover more from The Monitor
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Analysis
Four Killed in Beirut Hotel Strike, Israel Says It Targeted Iranian Commanders
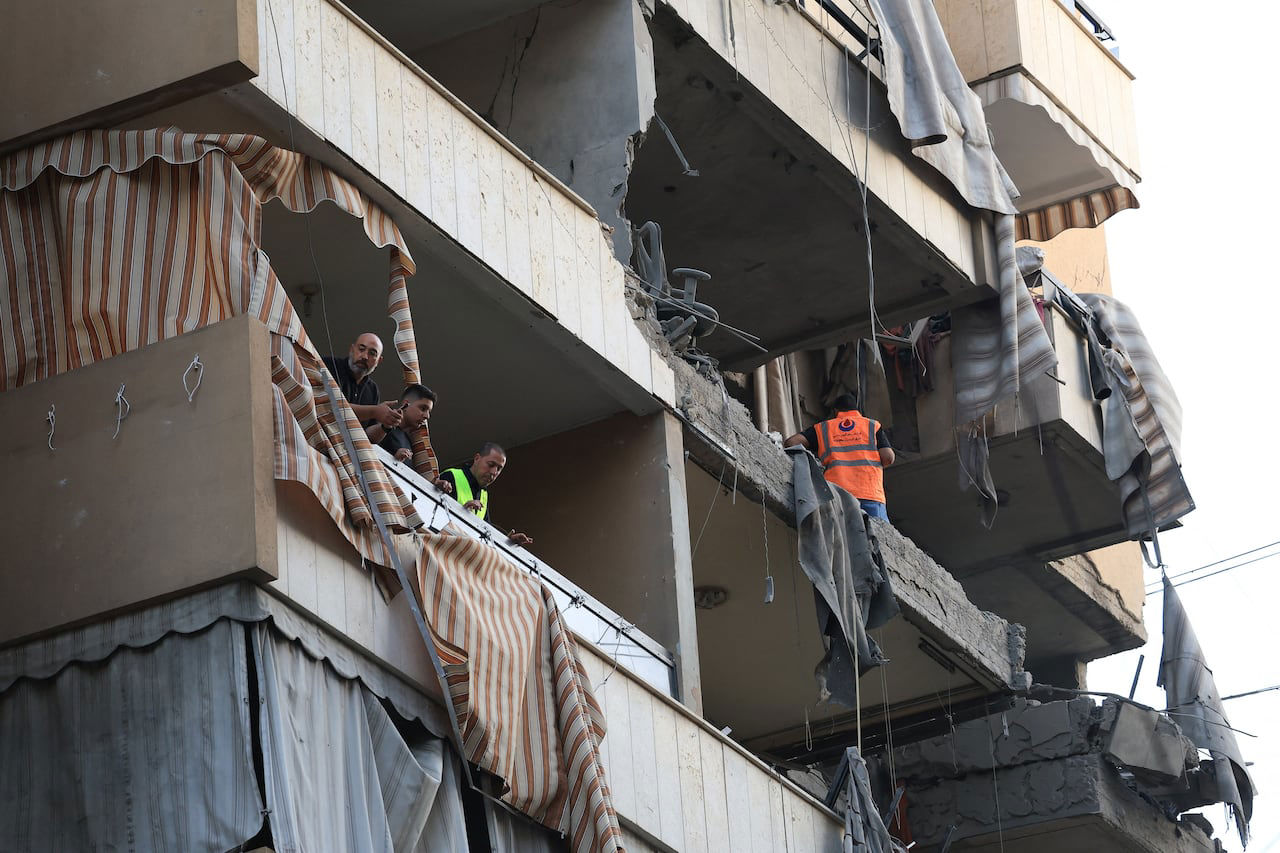

An Israeli precision strike on the Ramada hotel building in central Beirut early Sunday killed at least four people and wounded ten others, Lebanon’s Health Ministry confirmed, marking the first Israeli strike to hit the heart of Beirut since Israel-Hezbollah hostilities resumed last week. The Israeli military said it had targeted key commanders of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps’ (IRGC) Quds Force Lebanon Corps — an elite unit that serves as Iran’s primary operational bridge to Hezbollah — striking the Raouche seafront district that had, until now, remained an island of uneasy calm amid a rapidly escalating regional war. The strike is the latest in a devastating cascade of events that has reshaped the Middle East since the reported killing of Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei in joint US-Israeli strikes that began on February 28, 2026.
Table of Contents
Key Facts at a Glance
| Detail | Information |
|---|---|
| Date of Strike | Sunday, March 8, 2026 |
| Location | Ramada hotel building, Raouche (Rawche) district, central Beirut |
| Casualties | 4 killed, 10 wounded (Lebanese Health Ministry) |
| Israeli Stated Target | IRGC Quds Force Lebanon Corps commanders |
| Hotel Status | Also sheltering displaced families from southern Lebanon |
| Significance | First Israeli strike on central Beirut since hostilities resumed March 2 |
| Context | Part of broader US-Israel campaign (“Operation Epic Fury”) against Iran |
| Lebanon Displaced | 454,000 registered displaced since the war’s resumption |
| Second Hotel Strike? | Yes — a Hazmieh-area hotel was struck on March 4, 2026 |
A Strike That Shattered a Temporary Sanctuary
Before dawn on March 8, the quiet of Beirut’s Raouche waterfront — the palm-lined Mediterranean promenade famous for the towering Pigeon Rock sea stacks and a string of hotels that once drew tourists from Riyadh to Paris — was torn apart by an explosion. An Israeli precision munition struck an apartment on the fourth floor of the Ramada hotel building, shattering windows and scorching walls in a room that an AFP photographer who rushed to the scene described as a gutted shell of charred furniture and broken glass.
Lebanese security forces quickly cordoned off the area. Dozens of panicked guests — many of them families who had fled Israeli airstrikes on Beirut’s southern suburbs and the frontline towns of southern Lebanon — streamed out of the building carrying luggage and children, some in nightclothes, uncertain where to go next. Witnesses reported hearing a single thunderous blast before ambulances converged on the site.
The Lebanese Health Ministry confirmed the toll: four dead, ten wounded. It did not immediately release the identities of the victims, and it was not publicly known whether those killed included the Iranian commanders Israel said it was targeting, civilians sheltering at the hotel, or both.
Israel’s Justification: Quds Force Lebanon Corps in the Crosshairs
The Israeli military was unambiguous about its intent. In a formal statement, the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) said it had struck “key commanders of the Quds Force’s Lebanon Corps” — the IRGC’s extraterritorial operational arm that has long served as the principal organiser of Iran’s military support for Hezbollah. The IDF did not name the individuals it said were killed.
“The commanders of the Quds Force’s Lebanon Corps operated to advance terror attacks against the state of Israel and its civilians, while operating simultaneously for the IRGC in Iran,” the military said, adding that the Quds Force Lebanon Corps functions as the critical liaison between Tehran’s intelligence apparatus and Hezbollah’s military hierarchy — coordinating weapons transfers, training, and strategic direction for the Lebanese militant organisation.
The IDF said it employed precision weapons and pre-strike aerial surveillance to minimise civilian casualties, and reiterated a warning it has now issued repeatedly since hostilities resumed: Israel “will continue to precisely eliminate the commanders of the Iranian terror regime wherever they operate.”
Israel has not claimed to have struck a hotel accidentally. The framing — that IRGC commanders were embedded within a civilian hotel in one of Beirut’s most recognisable tourist districts — is consistent with a pattern of Israeli operations that has drawn intense international scrutiny: the assertion that Iranian and Hezbollah command structures deliberately position themselves within civilian infrastructure, using proximity to non-combatants as a form of operational protection.
The Broader War: How Lebanon Was Drawn Back In
To understand the Ramada strike, one must trace the chain of escalation back to the final days of February 2026.
Lebanon was drawn into the regional war on March 2, when Iran-backed group Hezbollah attacked Israel in response to the killing of Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei in the US-Israeli strikes that began on February 28 and have killed more than 1,300 people. That killing — described by Washington and Jerusalem as a decapitating blow against the Iranian theocracy — triggered what Hezbollah called a duty of retaliation, ending a fragile ceasefire that had held since November 2024.
Since then, Israel has launched multiple waves of strikes across Lebanon and sent ground forces into border areas. Lebanon’s Social Affairs Minister confirmed that 454,000 people had been registered as displaced since the outbreak of the new war, including 112,525 people registered in government shelters. Concurrently, Israeli operations have struck Iranian oil and military infrastructure directly inside Iran — including fuel storage facilities in Tehran described by the IDF as supporting military operations — while Iran has retaliated with missile barrages against Israel and drone strikes that have targeted Gulf states including Bahrain, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and the UAE.
Iran’s Revolutionary Guards have said the country could sustain an “intense war” with the United States and Israel for at least six months. Iranian President Masoud Pezeshkian has characterised Trump’s demand for “unconditional surrender” as a fantasy, vowing that Tehran “will be forced to respond” if neighbouring countries continue to be used as launchpads for attacks on Iranian territory.
The Sunday morning hotel strike must be read against this backdrop: a conflict that began as an operation against Iran’s nuclear programme and its supreme leadership has expanded, within days, into a multi-theatre war stretching from the Lebanese coast to the Gulf.
Raouche — A Tourist Jewel in the Line of Fire
Few places in Beirut carry as much symbolic weight as Raouche. The district, hugging the Mediterranean coastline on the city’s western edge, has long been the face Beirut presents to the world — a waterfront of hotels, seafood restaurants, and the silhouetted Pigeon Rock arches that feature on half the postcards sold in Lebanon. During the 2006 war with Israel, Raouche remained largely untouched. During the 2024 Israel-Hezbollah conflict, it functioned as a kind of informal sanctuary — crowded, anxious, but structurally intact.
The area along the Mediterranean coast is home to dozens of hotels, now overcrowded with displaced people who fled their homes elsewhere in Lebanon due to the ongoing fighting. This is the second Israeli attack on a hotel in the Beirut area this week.
That distinction — a civilian refuge striking another civilian refuge — now belongs to a past that feels very distant. The hotels of Raouche, many operating far above their normal capacity as they absorbed the displaced from Dahiyeh, Tyre, and Sidon, are no longer sanctuaries. For the families who fled the lobby of the Ramada in the hours after Sunday’s strike, there is no obvious place of safety left in central Beirut.
Geopolitical Analysis: The Logic and Risks of Striking in Plain Sight
Why Strike a Beirut Hotel?
From a strategic standpoint, the decision to strike a recognisable commercial building in central Beirut reflects a doctrine Israel has applied with increasing assertiveness since October 2023: the elimination of high-value targets regardless of their physical surroundings, justified by the claim that Iran deliberately embeds operational command structures within civilian infrastructure.
The Quds Force Lebanon Corps is not a peripheral element of Iran’s regional strategy. It is the connective tissue between Tehran’s grand design and Hezbollah’s battlefield capacity — responsible for smuggling advanced missile systems across the Syrian corridor, coordinating intelligence sharing, and providing strategic direction to Hezbollah’s leadership. If the individuals killed in Raouche on Sunday were indeed senior commanders of this unit, the operational disruption to Iran’s Lebanon network could be significant.
But there are serious risks embedded in this approach. Striking a hotel that was simultaneously serving as a shelter for displaced civilians — even if Iranian commanders were operating from within its walls — places Israel in a complex legal and moral position under international humanitarian law. Analysts and human rights organisations have noted that the principle of distinction, which requires parties to a conflict to discriminate between combatants and civilians, does not simply dissolve because a military actor embeds itself within civilian property.
The Deepening Iran-Israel-US Triangle
The Beirut hotel strike is one data point within a rapidly shifting strategic geometry. The killing of Khamenei has removed the single individual who, for decades, served as the arbiter of Iran’s strategic patience — the figure who decided when to escalate and when to absorb punishment. His absence creates a vacuum that the Revolutionary Guards, the hardline factions within the IRGC, and Hezbollah may seek to fill with more aggressive posturing, even as Iran’s conventional military capacity is being systematically degraded.
For Washington, the conflict presents a paradox. The Trump administration has provided intelligence support and munitions to Israel’s Iran campaign — including an emergency congressional bypass to approve a $650 million bomb sale — while simultaneously insisting that any political resolution requires a leadership in Tehran “acceptable” to Washington. That is not a peace process; it is regime change by another name, and it carries historical precedents that few in the region have forgotten.
Economic Shockwaves — Oil, Tourism, and a Fractured Region
The economic fallout from this conflict is already measurable. Crude oil prices have surged as markets price in the risk of sustained disruption to Iranian export capacity and potential spillover to Gulf infrastructure — fears given fresh urgency by Iranian drone strikes that have struck a water desalination plant in Bahrain and sent projectiles toward Fujairah’s oil facilities in the UAE.
For Lebanon, the economic consequences are catastrophic in a country that was already navigating one of the worst fiscal collapses in modern history. The hospitality and tourism sector — which had been showing tentative signs of recovery in late 2024 and early 2025 following the November ceasefire — has been effectively destroyed for the foreseeable future. International airline routes into Beirut Rafic Hariri International Airport have been suspended. Travel advisories from the United States, United Kingdom, European Union, and Gulf states urge citizens to leave or avoid Lebanon entirely.
The Raouche waterfront, which in better years drew hundreds of thousands of visitors annually, now hosts not tourists but the displaced — families in hotel rooms they cannot pay for, in a city whose banking system remains effectively paralysed, served by a government with no budget, no functioning army capable of confronting any of the parties to this conflict, and no clear diplomatic channel to any power with the leverage to broker a ceasefire.
Forward Implications: Escalation Thresholds and the Search for an Exit
The Ramada strike raises a question that has no comfortable answer: where does this conflict go next?
Israel has now demonstrated both the will and the capability to strike Iranian-linked targets in the very heart of Beirut — a city that Israeli military planners have historically treated as a threshold not to be crossed lightly, given the political and humanitarian consequences. That threshold is gone. Whether this represents a permanent shift in Israel’s operational doctrine for Lebanon, or a temporary posture tied to the extraordinary circumstances of the Khamenei killing and Operation Epic Fury, remains unclear.
Iran, for its part, is balancing two imperatives: the need to demonstrate to its domestic constituency — and to Hezbollah — that it has not been rendered strategically impotent by the loss of its supreme leader, and the cold calculation that escalating further against Israeli or American assets risks triggering a response that could threaten the regime’s physical survival. Iranian President Pezeshkian’s weekend statement — apologising to neighbouring states for the regional fallout while vowing to respond to further provocations — suggests Tehran is attempting to thread a needle between resistance and restraint.
What is clear is that the civilian populations caught between these forces — the four people killed in the Ramada, the 454,000 displaced across Lebanon, the families sleeping in school gymnasiums and overcrowded hotel rooms from Tyre to Tripoli — have no vote in these calculations, and no protection that the current international architecture has proven capable of providing.
Conclusion: The Heart of Beirut Is No Longer Safe
Sunday’s strike on the Ramada hotel is a milestone in a conflict that is rewriting the rules of engagement across the Middle East in real time. It signals that no geography in Lebanon — not the tourist districts of Raouche, not the hotels that shelter the displaced, not the symbolic heart of a capital that has already absorbed so much — is beyond the reach of Israeli precision munitions when Iran’s operational commanders are believed to be present.
The geopolitical architecture of the region — the Iran-Hezbollah axis, the ceasefire agreements, the unspoken de-escalation thresholds that governed the conduct of conflict for decades — is being dismantled faster than any diplomatic framework can be assembled to replace it. For the families who fled the Ramada lobby before dawn on Sunday, carrying children and luggage into an uncertain Beirut morning, that abstract geopolitical reality has a very specific and very human weight.
Discover more from The Monitor
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Analysis
The Mirage of a New Middle East: War With Iran Won’t Reshape the Region the Way America Wants
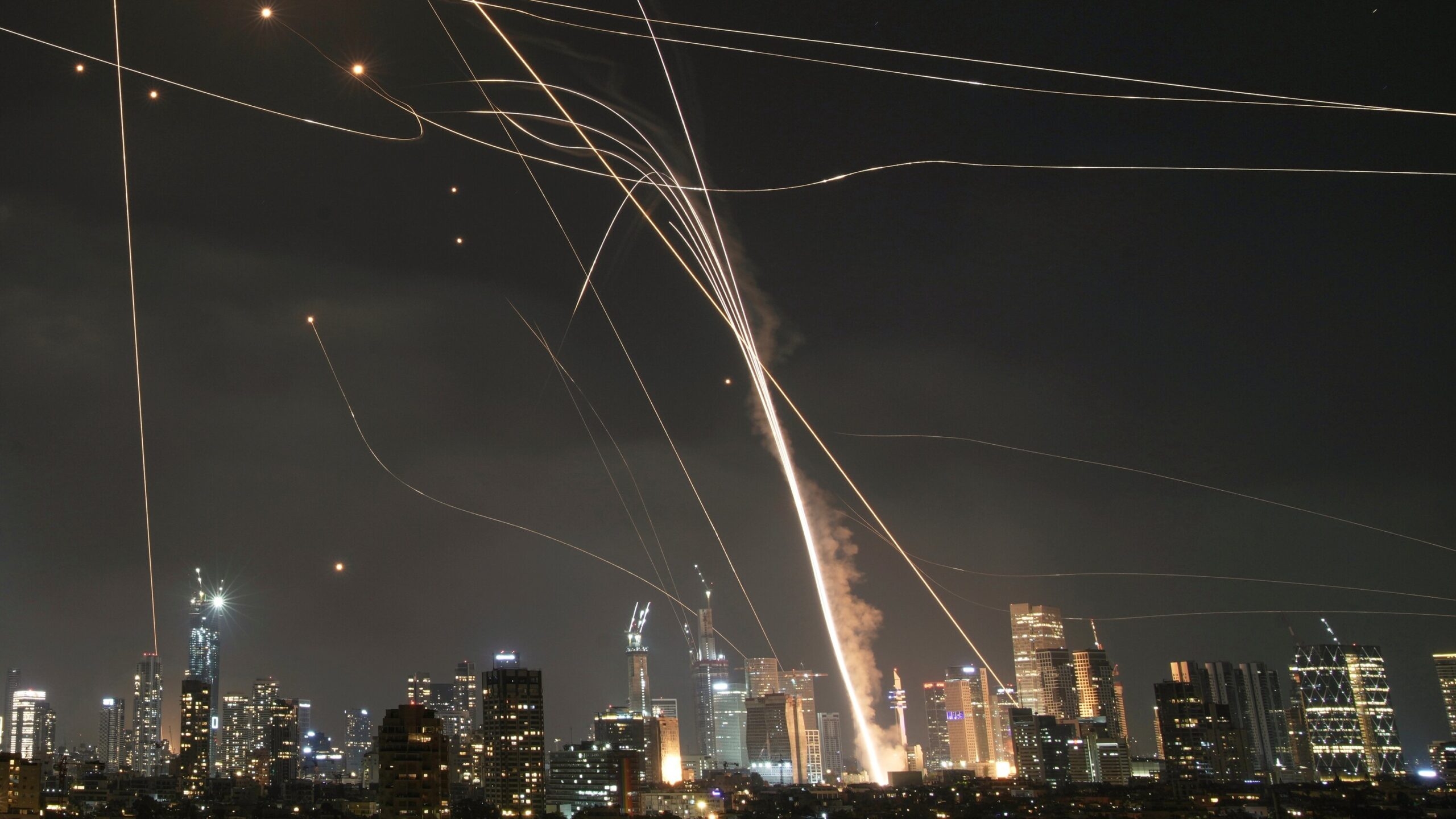

On the morning of February 28, 2026, at exactly 2:30 a.m. Eastern time, Donald Trump released an eight-minute video on Truth Social explaining why the United States had just begun bombing Iran. The message was characteristically blunt: regime change, existential threat, forty-seven years in the making. By sunrise, the Middle East was on fire—literally and strategically—and the world had entered a crisis that no amount of American airpower was ever going to resolve on Washington’s terms.
Eight days later, war with Iran has not reshaped the region the way America wants. It has produced something rather different: a global energy shock, a humanitarian catastrophe, and a geopolitical reckoning that exposes, with brutal clarity, the limits of military supremacy as a tool for political transformation.
Table of Contents
A Diplomatic Window, Deliberately Slammed Shut
The cruelest detail of this war is not its ferocity but its timing. On February 27, just twenty-four hours before the first American bombs fell on Tehran, Oman’s Foreign Minister Badr Al-Busaidi announced that a diplomatic “breakthrough” had been reached—that Iran had agreed in principle to never stockpile enriched uranium and to full international verification. A second round of nuclear talks had been scheduled for Geneva. The architecture of a deal was, by most accounts, within reach.
Instead, the Trump administration—which had spent weeks assembling the largest U.S. military presence in the Middle East since the 2003 invasion of Iraq—chose the strike package over the negotiating table. “The president was faced with a choice,” White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt told reporters. That framing, however politically convenient, obscures the harder truth: the choice had been engineered, not inherited. Washington’s preconditions—total cessation of uranium enrichment, dismantlement of Iran’s ballistic missile program—were conditions Tehran had explicitly and repeatedly said it could not accept. The diplomacy was theatre. The war was always the plan.
UN Secretary-General António Guterres, in a statement that may endure as this conflict’s moral verdict, described the strikes as “squandering” an opportunity for diplomacy. He was not wrong. He was, in the manner of UN secretaries-general throughout history, also completely powerless to stop it.
The Human Arithmetic of “Epic Fury”
Operation Epic Fury—the Pentagon’s somewhat grandiose codename for the campaign—has, by the morning of March 7, killed at least 1,332 people in Iran, of whom at least 181 are children, according to UNICEF. Schools have been struck—most infamously, a girls’ elementary school in Minab on the very first day of the campaign, killing at least 165 schoolgirls and staff. Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth has said only that the Pentagon is “investigating.”
The Center for Strategic and International Studies estimates the first 100 hours of the campaign cost $3.7 billion—roughly $891 million per day, with $3.5 billion of that entirely unbudgeted. US and Israeli forces have struck over 4,000 targets across Iran in the opening four days alone, a pace that war-monitoring group Airwars describes as “significantly more targets per day than any campaign in recent decades”—surpassing even the assault on Gaza that began in 2023, and the US-led campaign against ISIS.
Iran, for its part, is not lying down. Its Revolutionary Guard has launched twenty-three waves of missile and drone strikes against Israel, US bases across the Gulf, and civilian infrastructure from Riyadh to Doha to Dubai. Amazon Web Services’ Bahrain data center was taken offline after a nearby drone strike. An oil refinery in Bahrain was hit. Kuwait’s embassy operations have been suspended. A vessel was struck seven nautical miles east of Fujairah. More than 330,000 people have been forcibly displaced across the broader region. Six US servicemen have died.
Trump’s demand, as of March 6, is “unconditional surrender.” He has also announced his intention to personally select Iran’s next leader—explicitly ruling out Mojtaba Khamenei, the son of the Supreme Leader assassinated in the opening salvo. The gap between what the United States is doing and what it can actually achieve has rarely been so wide.
The Oil Shock: When Geopolitics Meets the Fuel Tank
The Iran war impact on global oil markets has been, by any historical measure, extraordinary. When the Strait of Hormuz—through which approximately 20 percent of the world’s daily oil supply and significant LNG volumes normally transit—effectively closed to commercial shipping, markets responded with a violence not seen in decades.
Crude tanker transits through the Strait fell from an average of 24 vessels per day to four ships on March 1—three of them Iranian-flagged. By March 5, the Joint Maritime Information Center reported traffic at “single-digit levels”. Over 150 tankers sat at anchor outside the strait. Protection and indemnity insurance was pulled entirely for March 5 transit, making the economics of passage impossible regardless of the physical risk.
The price response has been historic. West Texas Intermediate crude surged 35.63 percent across the week ending March 7—the largest weekly gain in the history of futures trading, dating to 1983. WTI closed at $90.90; Brent at $92.69. By Friday morning, WTI had briefly topped $86 for the first time since April 2024, and Oxford Economics noted it was up close to 30 percent since the start of the war and more than 55 percent from the January low. Barclays analysts warned clients that Brent could hit $100 per barrel by next week if tankers remain unable to traverse the Strait. UBS put a scenario for $120 Brent on the table.
Qatar’s energy minister, Saad al-Kaabi, provided what may prove the week’s most alarming single statement, telling the Financial Times that Gulf exporters would halt production entirely within days if tankers cannot pass the Strait—a scenario that could, in his words, spike oil to $150 a barrel and “bring down the economies of the world.” US retail gasoline prices have already jumped 32 cents a gallon in a single week to $3.31, the sharpest seven-day increase since Russia invaded Ukraine in 2022.
For central banks, the timing is diabolical. Brent has risen 36 percent since the start of the year, reigniting inflationary pressures just as monetary policymakers had hoped for clear air to cut rates. “The ongoing Iran conflict solidifies the case for many central banks to hold rates steady for now,” Nomura economists wrote in a note on Sunday. The Federal Reserve’s calculus, already complicated by domestic tariff-driven inflation, has become considerably darker.
Supply Chain Fracture Lines
The disruption extends well beyond crude oil. Iran war supply chain disruption is now running across multiple vectors simultaneously. About 10 percent of the world’s container ships are caught up in broader shipping backups, with cargo expected to begin piling up at ports and transshipment hubs in Europe and Asia. Qatar’s LNG production has been suspended—a serious blow to European winter reserves and Asian buyers who rely on the emirate as their third-largest LNG supplier. European natural gas prices nearly doubled within 48 hours, peaking above €60/MWh before partially retreating on tentative Iranian signals about talks. Aviation over the Gulf has been disrupted, with multiple carriers rerouting long-haul flights and Kuwait’s US embassy evacuated following direct strikes.
Why the Region Won’t Be “Reshaped” on Washington’s Terms
The Fallacy of the “Day After”
Every war of choice arrives with a theory of the peace that follows. In 2003, it was Iraqi democracy radiating stability across the Arab world. In 2011, it was Libyan liberation opening a new chapter for North Africa. The Trump administration’s theory—as Trump himself sketched it on Truth Social, promising to make Iran “economically bigger, better, and stronger than ever before” once it surrenders and accepts a US-selected leader—follows this tradition with striking fidelity, and with equally striking ignorance of its failures.
Iran is not Iraq in 2003. It is a nation of 90 million people with a coherent national identity, deep institutional roots, and a military-theological establishment that has spent four decades preparing for precisely this scenario. Ali Larijani, secretary of Iran’s Supreme National Security Council, warned this week that Iranian forces are “waiting” for a potential US ground invasion, and are prepared to “kill and capture thousands of US troops.” These are not empty words from a cornered regime. They are the considered statements of a state that has fought a grinding eight-year war with Iraq, absorbed decades of sanctions, and internalized—perhaps more deeply than any nation on earth—what existential threat feels like.
The critical intelligence failure lies not in underestimating Iran’s missile inventory, but in misreading how regime existential pressure changes behavior. As one geopolitics analyst put it plainly this week: “If the regime feels threatened, it’ll lash out harder than it would if it thought it could ride out the attacks.” The logic of “maximum pressure” assumes a linear relationship between military pain and political capitulation. Iran’s history suggests the relationship is inverse.
The Gulf States: Caught, Not Converted
Washington’s implicit assumption—that its Gulf Arab partners would welcome an Iran humbled or broken—has collided with a reality more complicated and more dangerous. Saudi Arabia and the UAE did not ask for Iranian missiles to rain on their territory. Riyadh’s US embassy has been struck. Bahraini refineries are on fire. Qatar, which hosts the largest US airbase in the region at Al Udeid, has intercepted multiple waves of Iranian attacks. Saudi Arabia confirmed Iranian strikes on Riyadh and its Eastern Province.
The Gulf states are, in the most literal sense, collateral damage in a war prosecuted in part on their behalf—and at their lobbying. The Washington Post reported that Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman conducted multiple phone calls with Trump urging him to strike, warning that Iran would “become stronger and more dangerous if Washington did not strike immediately.” The irony now is that MBS’s kingdom is absorbing Iranian missiles while its energy exports sit stranded in tankers outside a closed strait. “Years of Iranian détente-building with the Gulf may be over,” noted Aysha Chowdhry of The Asia Group. That observation, though accurate, understates the fragility: Gulf states that were mending ties with Tehran in 2023—via Chinese mediation—are now war zones.
China’s Strategic Patience
Beijing’s response to this crisis has been a masterclass in what might be called strategic restraint with strategic benefit. China has loudly condemned the strikes—Foreign Minister Wang Yi called the assassination of Khamenei “a grave violation of Iran’s sovereignty” and demanded an immediate halt to military operations—but has offered Tehran nothing beyond rhetoric. The reason is pragmatic: Beijing was not notified of the strikes in advance, and faces its own acute disruption from the Strait closure, given that roughly half of China’s seaborne crude imports transit through the waterway.
Yet the strategic calculus cuts both ways. China has barred the export of rare earth elements for military use—materials crucial for everything from missiles to fighter jets—which complicates America’s capacity to replenish weapons at a historically unprecedented pace of consumption. And with US military attention and resources diverted deep into the Persian Gulf, the Indo-Pacific breathing room Xi Jinping gains is, from his perspective, a strategic dividend. “China is a fair-weather friend—long on words, short on risk,” observed Craig Singleton of the Foundation for Defense of Democracies. But in geopolitics, fair-weather friends who watch their rivals bleed are often the ultimate winners.
The Carnegie Endowment for International Peace captured Beijing’s posture with precision: China has always maintained productive relations with Iran, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Turkey, and Egypt simultaneously—a portfolio diversification that no other external power has matched. The war that Washington hoped would consolidate American primacy in the Middle East may, paradoxically, accelerate the region’s pivot toward Chinese mediation as the only broker trusted by all sides.
The Strategic Cost: What America Is Burning Through
The arithmetic of this campaign deserves more scrutiny than it has received. The US military has struck more than 3,000 targets in Iran and destroyed 43 Iranian warships since February 28. Iran’s ballistic missile attacks have, by the Pentagon’s own account, fallen 90 percent from peak—evidence of serious degradation. But Iran still fights. Its drone attacks have dropped only 83 percent. Its 23rd wave of missile strikes was announced this week. Its ground forces remain intact and warn of consequences for any invasion.
The weapons expenditure rates are almost certainly unsustainable. The US arsenal of precision munitions—stretched by support for Ukraine and the 2025 twelve-day war with Iran—is being consumed at a pace that no industrial base can immediately replace. China’s rare-earth export ban is not a symbolic gesture; it is a targeted intervention in America’s ability to keep this campaign going. The Senate’s vote on the War Powers Act—which failed, allowing Trump to continue the campaign—has done nothing to resolve the fundamental strategic question: what does “victory” actually look like, and who governs Iran the morning after?
Trump’s stated answer—a “great and acceptable leader” selected with direct US involvement—is not a policy. It is a fantasy that ignores every lesson of nation-building from Kabul to Baghdad to Tripoli. The Supreme Leader’s potential successor, Mojtaba Khamenei, has been explicitly ruled out by Washington. But Washington does not control Iranian succession. The IRGC, battered and enraged, retains both weapons and institutional memory. The Iranian people, who have no affection for the theocracy that has suppressed them for decades, have even less affection for foreign-imposed rulers.
The Forward Reckoning
Iran retaliation impact on global oil markets 2026 has become the dominant variable in the world economy. But the longer arc of this crisis will be measured in different currencies: the legitimacy of the international order, the durability of US alliances, the patience of Asian economies for disruption in their energy arteries, and the strategic positioning of China as the region’s indispensable mediator.
The path out of this war is not a military one. It is a negotiated one, and the very actors Washington has alienated—Oman’s mediators, Europe’s diplomats, China’s back-channels—are the ones who will ultimately have to construct it. Trump’s demand for “unconditional surrender” is not a negotiating position. It is a formula for indefinite war with a nation of 90 million that has nowhere left to retreat.
History is not kind to the architects of unnecessary wars. The mirage of a new Middle East—stable, American-aligned, Iran-free—has always been precisely that: a trick of desert light, receding as you approach it. The region’s fractures are not Iran-made. They are decades in the making, drawn in colonial borders and sustained by strategic miscalculation. No air campaign, however historic in its pace, changes those underlying geometries.
“What this conflict has changed, definitively and dangerously, is the price at the pump, the temperature of the global economy, and the degree of trust that the international community extends to American statecraft. “
Those are not small things. They are, in the medium term, the very foundations of the influence Washington is trying, through force, to reassert.
The Middle East will be reshaped by this war. Just not in any way that Washington planned, or that any American president will be proud to claim.
Discover more from The Monitor
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
-

 Featured5 years ago
Featured5 years agoThe Right-Wing Politics in United States & The Capitol Hill Mayhem
-

 News4 years ago
News4 years agoPrioritizing health & education most effective way to improve socio-economic status: President
-

 China5 years ago
China5 years agoCoronavirus Pandemic and Global Response
-

 Canada5 years ago
Canada5 years agoSocio-Economic Implications of Canadian Border Closure With U.S
-

 Democracy5 years ago
Democracy5 years agoMissing You! SPSC
-

 Conflict5 years ago
Conflict5 years agoKashmir Lockdown, UNGA & Thereafter
-

 Democracy5 years ago
Democracy5 years agoPresident Dr Arif Alvi Confers Civil Awards on Independence Day
-

 Digital5 years ago
Digital5 years agoPakistan Moves Closer to Train One Million Youth with Digital Skills
















